NETWORK EVENTS
17 December 2025
SAX-QT Quantum Saxony officially launched!
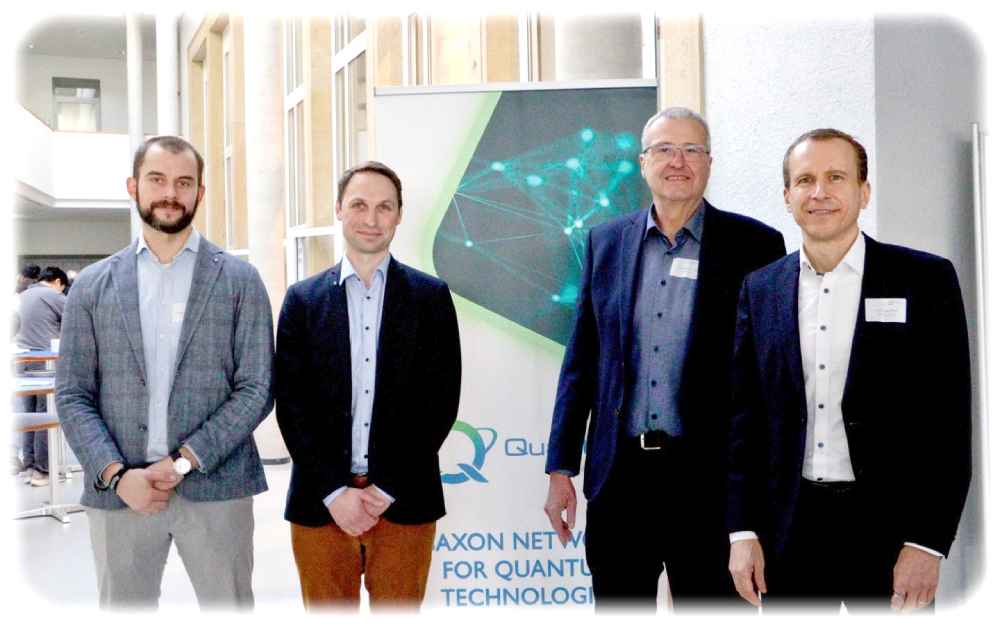

Die Projektpartner Dr. Benjamin Lilienthal-Uhlig (Fraunhofer-Institut IPMS), Albrecht Hänel (Fraunhofer-Institut IWU), Prof. Dr. Bernd Büchner (Leibniz-Institut IFW) und Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jörg Lässig (Hochschule Zittau/Görlitz) eröffnen das SAX-QT Sächsische Forschungsnetzwerks für Quantentechnologien (Foto: A.-J. Zichner, Fraunhofer IPMS)
December 2025
SAX-QT Quantum Saxony OFFICIAL LAUNCH 17.12.2025
17 December 2025, 14:00-16:00
Official launch and presentation of the EFRE network SAX-QT – Quantum Saxony
Check here for the Program and Registration.
See here the press release by Heiko Weckbroadt @Oiger.
December 2025
Winter Quantum Colloquium 17. & 18.12.2025
We are pleased to invite you to the first SAX-QT Winter Quantum Colloquium on 17–18 December 2025 at the IFW Dresden.
Quantum workshop with interesting tutorial talks given by our network partners
Don’t miss the opportunity to become a part of Quantum Saxony and to learn something new about the Quantum World!
Check here for the Program and Registration.
September 2025
SAX-QT Quantum Saxony Kick-off Meeting
On September 29, 2025, we held the Kick-off meeting of the SAX-QT, the Saxon Research Network for Quantum Technologies. Partners from all over Saxony came together to jointly shape the future development of an interdisciplinary network Quantum Saxony, including research and industrial partners.
June 2025
SaxonQ's Mobile Quantum Computer in Operation
We’re proud to celebrate SaxonQ GmbH on supplying a new 4-qubit mobile quantum computer to Fraunhofer IWU’s Dresden branch. Since June, this system has been supporting the Saxon Research Network for Quantum Technologies (SAX-QT) in exploring new quantum applications.
The device will help advance Industry 4.0 and cognitive production solutions, benefiting sectors like automotive and aviation, while strengthening regional quantum innovation.
March 2025
Saxon EFRE/JTF-Research Networks Kick-off
On March 4, 2025, the official kick-off event for the research networks supported by the ERDF/JTF funding program InfraProNet 2021–2027 took place in Dresden. A total of seven research networks are benefiting from this funding. They cover key future fields, including bioelectronics, energy-autonomous ICT technologies, artificial intelligence in medicine, fusion research, quantum technologies, security research, and robotics.
See more by the Center for Medical Informatics and at sachsen.de
NETWORK GOALS
The Saxon Quantum Technologies Research Network primarily focuses on the future development of resource-efficient, environmentally friendly, and energy-saving quantum materials and technologies "Made in Saxony", driving progress in this field.
Various competencies for advancing research and innovation, including young talents, will be linked to establish a powerful "quantum community" in Saxony and secure the long-term demand for this future technology.
THE SAX-QT PROJECT
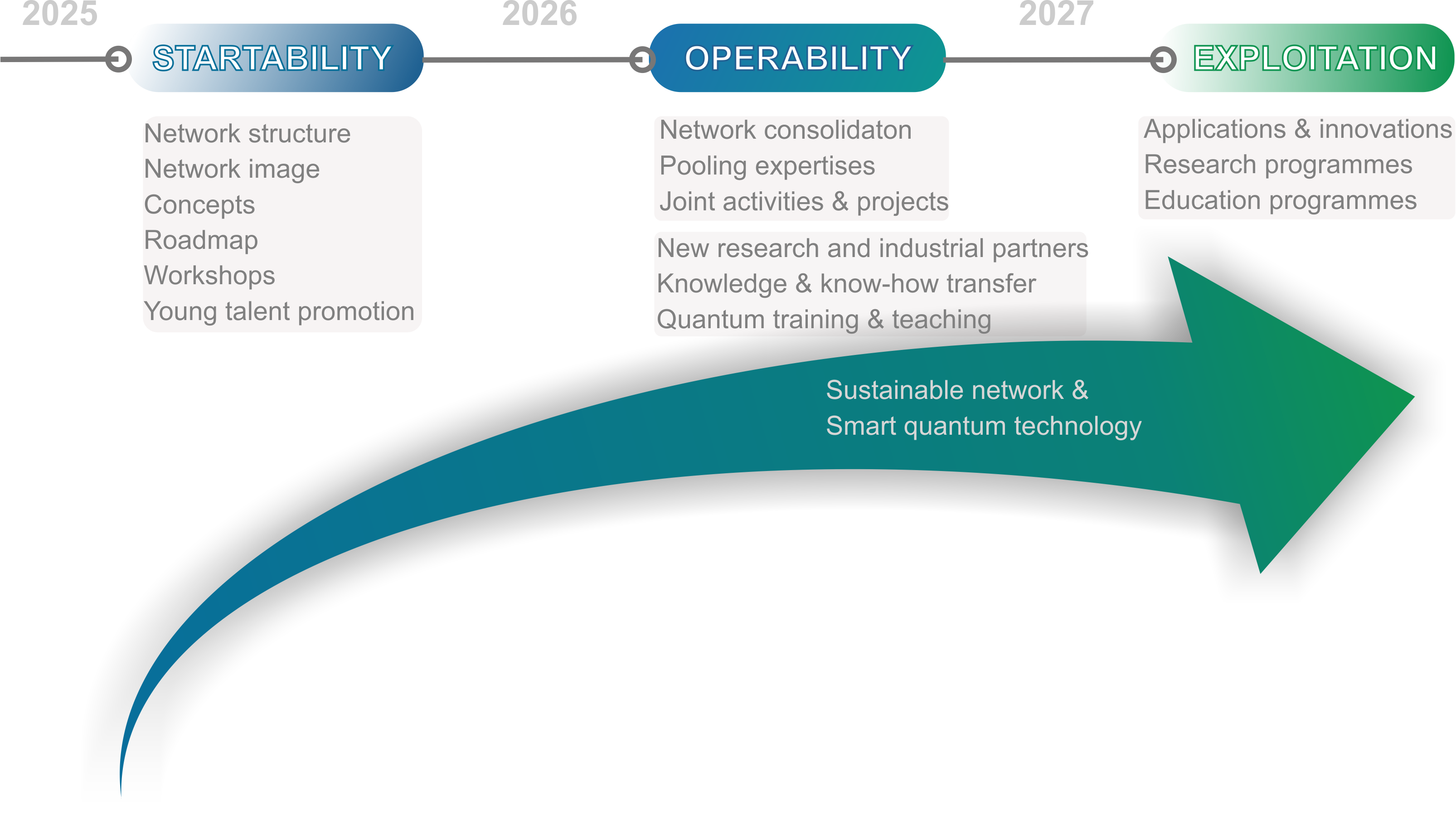
Project Timeline
The SAX-QT initiative spans three phases towards the establishment of a future, permanent Saxon Quantum technology network.
Project Consortium
During the period 2025-2027, the SAX-QT project team will establish, promote, and coordinate a powerful Saxon network of quantum technologies, bringing together research and industrial experts.
Focus Education, Research and Knowledge Transfer
The University of Applied Sciences Zittau/Görlitz (HSZG) contributes significantly to applied quantum research, particularly with its expertise in computer science and software engineering. The HSZG offers compulsory courses in quantum computing and quantum AI to reflect the importance and innovative power of these technologies. HSZG assumes lead coordination of the network.
Role:
The HSZG acts as a multiplier for knowledge transfer, along with ensuring the security of the network, conveying this promising expertise to researchers, companies, teachers, students, and pupils.


Focus Industrial Applications
In close cooperation with Fraunhofer Institute for Machine Tools and Forming Technology (IWU), the Fraunhofer Institute for Photonic Microsystems (IPMS) focuses on collaboration with industrial partners. It will primarily coordinate connections to the microelectronics and semiconductor industries, as well as positioning for large-scale European quantum technology projects, such as pilot lines in the European Chips Act (ECA). IPMS analyzes problem sets and application scenarios of partners and develop together pilot solutions using state of the art quantum machines of our technology collaborators.
Role:
Fraunhofer is linking the business and industry to the future application of quantum computing technology in innovative products and services.

Focus Quantum Materials Research
The Leibniz Institute for Solid State and Materials Research Dresden (IFW) coordinates activities in the field of basic and materials research for new quantum technologies. A key focus is the exploration of new materials and phenomena that may be promising for applications in quantum technology and it is one of the leading research institutes in this field.
Role:
The IFW's research strategy is based on the motto "Materials for Technologies of the Day After Tomorrow" and aims to generate new scientific insights and develop new functionalities and applications.
& Network
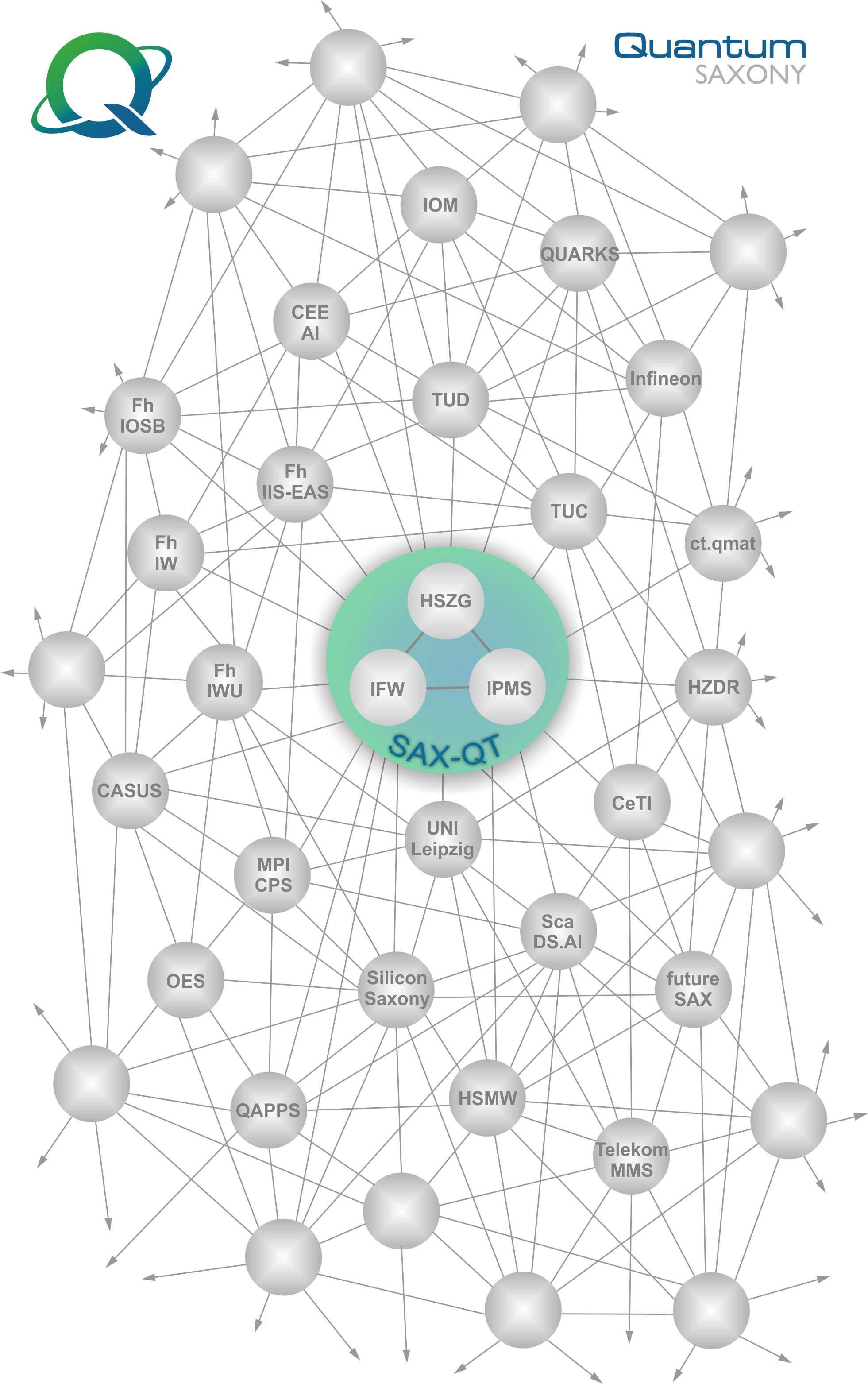
PARTNERS
Quantum Saxony collaborates with numerous institutions, clusters, and networks with a specific focus and various interests to approach the field of quantum technology from different aspects.
QUANTUM TECHNOLOGY
Quantum technologies represent a rapidly evolving interdisciplinary field that applies the fundamental principles of quantum mechanics, such as superposition, entanglement, and quantum tunnelling, to develop transformative tools for science and industry. They encompass a wide spectrum of research areas, including quantum computing, which uses qubits to perform complex computations beyond the reach of classical systems; quantum communication, which enables ultra-secure information transfer through quantum key distribution; and quantum sensing and metrology, which achieve unprecedented precision in measuring time, gravity, and electromagnetic fields.
Equally vital are quantum materials and devices, where the exploration of superconductors, semiconductors, and topological materials drives the development of next-generation components for computing and information technologies. These areas are complemented by quantum simulation, which allows researchers to model and understand complex quantum systems such as molecules or condensed matter.
Together, these domains form a unified scientific frontier that bridges physics, computer science, materials engineering, and information theory. By translating quantum principles into real-world applications, quantum technologies aim to establish a foundation for secure communication infrastructures, sustainable computing architectures, and highly sensitive measurement systems, ushering in a new era of technological innovation and discovery.
Network Focus Fields
The SAX-QT initiative unites three focus fields of quantum technology as mentioned below.
Quantum materials and systems
Quantum materials are solids that exhibit unique quantum phenomena stemming from unconventional spin interactions, electronic correlations, electron-photon interactions, and/or topological band structures. Notable examples of these phenomena include superconductivity and magnetism. Additionally, quantum effects play a significant role in materials constrained to the nanometer scale, such as nanoparticles, thin films, and nanotubes.
Quantum computing, sensors, photonics
The idea of quantum computing originates from ideas of Paul Benioff, Yuri Manin and Richard Feynman with the central idea of simulating quantum mechanical systems efficiently.
Today there are hybrid quantum-classical algorithms for the simulation of quantum systems available and can be applied to the simulation of molecules, the development of drugs, nano-technology or new materials
Education, outreach, and transfer
By connecting microelectronics with industry, quantum technology research outcomes are translated into practical applications more efficiently. Specifically, SAX-QT launches collaborative pilot projects and seminars, as well as various networking and knowledge transfer activities. It strengthens talent development through initiatives, such as doctoral schools, qualifications, and outreach programs. This approach fosters a thriving quantum community in Saxony that gains international recognition.
QUANTUM SAXONY HUB
The SAX-QT initiative aims to bring Quantum Technology into demonstrators, pilot solutions, and, finally, productive practical applications.
We offer our partners the following services:
- Screening of an industry or application field for applications and solutions that can potentially benefit from quantum technology solutions or are targets of disruptive developments connected to it.
- Education of specialists working in industry in quantum materials, quantum programming and quantum software development, addressing the up-to-date quantum materials, quantum computing software frameworks and hardware solutions in cooperation with our technology partners.
- Cooperative research and development of showcase and pilot solutions in the industrial sector or the application field of the cooperation partner.